What is the Wealthiest City in Iraq? A Comprehensive Guide to Baghdad’s Economic Dominance

What is the Wealthiest City in Iraq?
Introduction
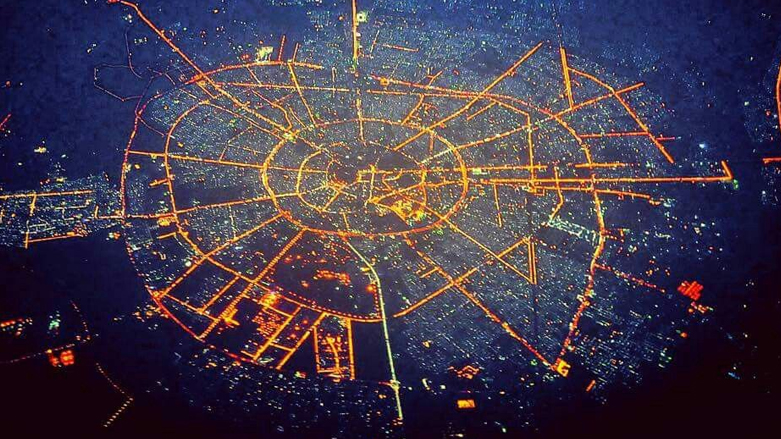
Iraq’s economic landscape has undergone significant transformation throughout its long history, from ancient Mesopotamian trade centers to modern urban economies shaped by oil wealth, conflict, and reconstruction. When examining the wealthiest city in Iraq, Baghdad stands as the undisputed economic powerhouse of the nation. As Iraq’s capital and largest metropolitan area, Baghdad dominates the country’s economic activities, serving as its financial, commercial, and industrial hub. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what makes Baghdad Iraq’s wealthiest city, examine other economically significant Iraqi urban centers, and provide insights into the factors driving wealth distribution across the country.
Baghdad: Iraq’s Economic Center
Historical Economic Significance
Baghdad’s wealth isn’t a modern phenomenon. Founded in 762 CE as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, the city quickly became one of the world’s most prosperous urban centers during the Islamic Golden Age. Its strategic location along the Tigris River established it as a critical node in trade networks connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe. This historical foundation as a commercial center continues to influence its economic prominence today.
Current Economic Status
Baghdad currently accounts for approximately 40% of Iraq’s GDP despite representing about 25% of the country’s population. This economic concentration reflects Baghdad’s role as:
- The center of Iraq’s government operations and public sector employment
- Headquarters for major national and international corporations operating in Iraq
- Home to the country’s largest financial institutions and Iraq Stock Exchange
- The primary recipient of reconstruction funds and development projects
- The main transportation and logistics hub for the nation
Key Economic Indicators
Baghdad’s wealth relative to other Iraqi cities is evident across multiple economic indicators:
- Per capita income: Baghdad’s average household income exceeds other Iraqi cities by 30-45%
- Property values: Real estate in central Baghdad commands prices 3-5 times higher than comparable properties in other major Iraqi cities
- Banking activity: Over 60% of Iraq’s banking transactions occur in Baghdad
- Business registration: Approximately 55% of new businesses in Iraq register in Baghdad
- Retail spending: Consumer spending in Baghdad outpaces other cities by significant margins
Factors Contributing to Baghdad’s Wealth
Government and Administrative Centralization
As Iraq’s capital, Baghdad houses virtually all major government institutions, ministries, and administrative bodies. This centralization creates thousands of public sector jobs and attracts secondary businesses that serve government operations. The concentration of political power also influences investment decisions, often directing development funds toward the capital region.
Oil Industry Connections
While Baghdad itself doesn’t sit directly on Iraq’s major oil fields, it serves as the administrative and financial center for the country’s petroleum industry. Most major oil companies maintain their Iraqi headquarters in Baghdad, and the Ministry of Oil, which oversees the nation’s most valuable natural resource, operates from the capital. This creates a substantial flow of oil wealth into the city’s economy.
Investment and Development Focus
Baghdad receives a disproportionate share of both public and private investment compared to other Iraqi cities. International aid, reconstruction projects, and private sector development have historically concentrated in the capital, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of economic growth and wealth accumulation.
Infrastructure Advantages
Baghdad benefits from the most developed infrastructure in Iraq, including:
- Superior transportation links (international airport, highway connections)
- More reliable electricity and water services
- Better telecommunications infrastructure
- Higher concentration of educational and healthcare facilities
These advantages make Baghdad more attractive for businesses and wealthy individuals, further concentrating economic activity.
Other Wealthy Cities in Iraq
While Baghdad clearly dominates Iraq’s economic landscape, several other cities contribute significantly to the nation’s wealth:
Basra: The Oil Capital
Basra, located in southern Iraq, ranks as the second wealthiest city in the country. Its economic strength derives primarily from:
- Proximity to Iraq’s largest oil fields
- Access to the Persian Gulf through the Shatt al-Arab waterway
- Status as Iraq’s only major port city
- Growing petrochemical industry
Despite these advantages, Basra’s wealth distribution remains highly uneven, with stark contrasts between oil industry areas and underdeveloped neighborhoods.
Erbil: Kurdistan’s Economic Hub
Erbil (also known as Hawler), the capital of Iraq’s Kurdistan Region, has emerged as an increasingly prosperous city, especially since the early 2000s. Its economic growth stems from:
- Relative security and stability compared to other parts of Iraq
- Autonomous governance allowing business-friendly policies
- Significant foreign investment, particularly in real estate and hospitality
- Growing tourism sector within the Kurdistan Region
- Development of local oil and gas resources
Erbil’s economic development has transformed it into what some call “the new Dubai” of Iraq, though recent challenges have somewhat tempered this growth.
Najaf and Karbala: Religious Tourism Centers
The twin holy cities of Najaf and Karbala in south-central Iraq generate substantial wealth through religious tourism. As sites of immense significance to Shia Muslims worldwide, these cities:
- Attract millions of pilgrims annually
- Support extensive hospitality and service industries
- Benefit from religious endowments and donations
- Maintain relatively stable economies even during periods of national turmoil
The religious tourism sector creates a distinctive economic profile for these cities, with wealth concentrated among religious institutions and businesses serving pilgrims.
Economic Challenges Facing Iraqi Cities
Despite Baghdad’s relative wealth, it—like all Iraqi cities—faces substantial economic challenges:
Infrastructure Deficiencies
Decades of conflict have severely damaged Iraq’s infrastructure. Even in Baghdad, frequent power outages, water supply problems, and inadequate public services remain common. These deficiencies limit economic productivity and quality of life.
Security Concerns
Although security has improved since the height of sectarian violence, ongoing concerns about stability continue to deter investment and economic development in Baghdad and throughout Iraq.
Wealth Inequality
Baghdad exhibits extreme wealth disparity, with luxurious neighborhoods and commercial districts existing alongside impoverished areas with inadequate services. This inequality creates social tensions and limits inclusive economic growth.
Economic Diversification
Baghdad’s economy, like Iraq’s overall, remains heavily dependent on oil revenues and government spending. Limited economic diversification makes the city vulnerable to oil price fluctuations and public sector budget constraints.
Future Economic Outlook for Baghdad and Iraq
Looking ahead, Baghdad’s economic trajectory will likely be shaped by several key factors:
Reconstruction and Development Initiatives
Ongoing reconstruction efforts present opportunities for economic revitalization in Baghdad. The success of these initiatives will significantly impact the city’s future prosperity.
Oil Market Dynamics
As Iraq’s economy remains heavily petroleum-dependent, global oil price trends and Iraq’s production capacity will continue to influence Baghdad’s economic health.
Political Stability
Baghdad’s economic prospects are inextricably linked to Iraq’s broader political stability. Improvements in governance and security would create more favorable conditions for economic growth.
Diversification Efforts
The Iraqi government has acknowledged the need to diversify beyond oil dependence. Baghdad, with its concentration of human capital and institutions, could play a pivotal role in developing new economic sectors.
Tips for Business and Investment in Baghdad
For those considering business or investment opportunities in Baghdad, several practical considerations apply:
- Local partnerships: Forming relationships with established local businesses can help navigate regulatory complexities and cultural nuances.
- Security planning: Despite improvements, comprehensive security planning remains essential for business operations in Baghdad.
- Infrastructure solutions: Businesses should prepare alternative solutions for infrastructure challenges, such as backup power generation.
- Sector selection: The most promising sectors currently include construction, logistics, consumer goods, and services supporting government and oil industry operations.
- Regional expansion: Consider using Baghdad as a base for operations that eventually extend to other Iraqi cities and markets.
Conclusion
Baghdad undeniably stands as Iraq’s wealthiest city, benefiting from its historical role, political centralization, and connection to the oil industry. However, this wealth exists alongside significant challenges, including infrastructure deficiencies, security concerns, and pronounced inequality. The future economic trajectory of Baghdad—and by extension, Iraq—will depend on addressing these challenges while capitalizing on the city’s substantial human capital and strategic importance.
As Iraq continues its post-conflict reconstruction and development, Baghdad will likely maintain its position as the nation’s economic center. The real question is whether this wealth can be distributed more equitably and sustainably, both within the capital and throughout the country.
























































* * * Win Free Cash Instantly: https://qiblah.com.kw/index.php?oeopnr * * * hs=56dfc8da402c64d5dfcffafa92d3fd3a* ххх*
03rd May 2025Your comment is awaiting moderation.
69h9vp