How Does the Private Sector Contribute to Iraq’s Economy?

How Does the Private Sector Contribute to Iraq’s Economy?
Introduction
The private sector is a critical component of Iraq’s economy, driving growth, innovation, and employment. Despite the country’s reliance on oil and gas, the private sector has emerged as a significant force in diversifying the economy and fostering sustainable development. This article delves into the contributions of the private sector to Iraq’s economic landscape, providing valuable insights, current data, and practical tips for stakeholders. We will explore how businesses, both small and large, are shaping the future of Iraq’s economy and what challenges and opportunities lie ahead.
The Role of the Private Sector in Iraq’s Economy
Diversification and Economic Stability
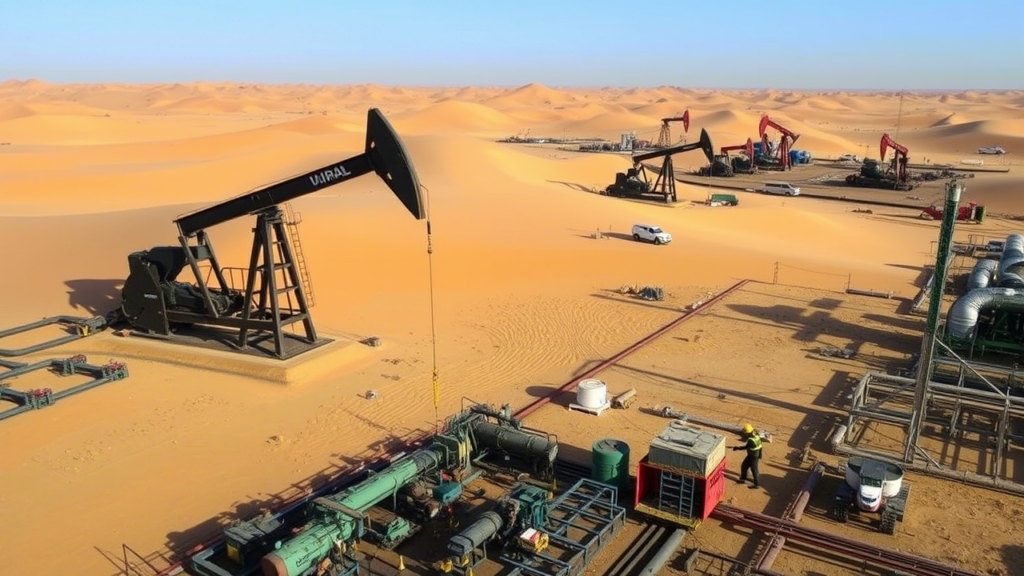
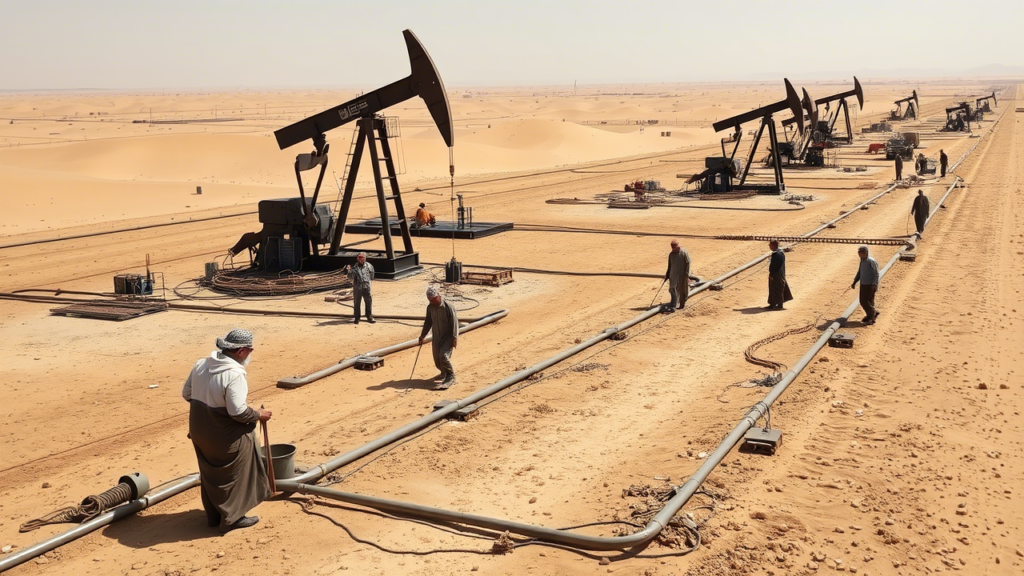
- Reducing Dependency on Oil: Iraq has long been dependent on oil revenues, which account for a significant portion of its GDP. The private sector offers a crucial alternative by investing in non-oil industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
- Creating Jobs: The private sector is a major employer, providing jobs for a large segment of the population. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly important in this regard, offering opportunities for entrepreneurship and skill development.
- Innovation and Technology: Private businesses are at the forefront of introducing new technologies and innovative practices, which can help modernize Iraq’s economy and make it more competitive globally.
Key Sectors of the Private Sector
Agriculture
- Investment in Modern Farming: The private sector has been instrumental in modernizing Iraq’s agricultural sector. Companies are investing in advanced farming techniques, such as precision agriculture and hydroponics, to increase productivity and sustainability.
- Food Processing and Export: Private firms are also involved in food processing and export, leveraging Iraq’s rich agricultural resources to create value-added products and tap into international markets.
Manufacturing
- Industrial Development: The manufacturing sector is experiencing a resurgence, with private companies setting up factories and production units. This includes industries such as textiles, construction materials, and automotive parts.
- Supply Chain Integration: Private manufacturers are integrating into global supply chains, which not only increases their competitiveness but also boosts the country’s export potential.
Services
- Healthcare and Education: The private sector is playing a vital role in improving access to healthcare and education. Private hospitals, clinics, and educational institutions are filling gaps left by the public sector and providing higher-quality services.
- Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions are crucial for economic growth, providing credit, investment, and insurance services that support business activities and consumer spending.
Challenges Faced by the Private Sector in Iraq
Political Instability and Security Concerns
- Investment Risks: Political instability and security concerns are significant deterrents to foreign and domestic investment. Businesses often face difficulties in ensuring the safety of their operations and personnel.
- Policy Uncertainty: Frequent changes in government policies and regulations can create uncertainty and make it challenging for businesses to plan and execute long-term strategies.
Bureaucratic Hurdles
- Complex Regulatory Environment: Navigating the bureaucratic landscape in Iraq can be cumbersome. Lengthy approval processes, vague regulations, and inconsistent enforcement are common issues.
- Corruption: Corruption remains a significant challenge, affecting the efficiency and fairness of business operations. Companies may face additional costs and delays due to corrupt practices.
Infrastructure Gaps
- Lack of Basic Infrastructure: Adequate infrastructure, including roads, electricity, and water supply, is essential for the private sector to operate efficiently. Many areas in Iraq still lack these basic facilities.
- Logistical Challenges: Inadequate transportation and logistics infrastructure can increase costs and reduce the competitiveness of businesses, especially those in the manufacturing and export sectors.
Opportunities for the Private Sector in Iraq
Government Support and Reforms
- Economic Reforms: The Iraqi government has initiated several economic reforms aimed at reducing the state’s role in the economy and fostering a more business-friendly environment. These reforms include simplifying regulatory processes, reducing bureaucracy, and providing tax incentives.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): The government is increasingly open to PPPs, allowing private companies to collaborate on infrastructure projects and other initiatives that can drive economic growth.
Emerging Markets
- Renewable Energy: Iraq has the potential to become a leader in renewable energy, particularly solar power. Private companies can capitalize on this by investing in solar farms and energy storage solutions.
- Technology and Innovation: The tech sector is growing, driven by the increasing use of digital services and the rise of startups. Private firms can leverage this trend by developing innovative products and services.
International Collaboration
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Iraq is actively seeking FDI to boost its private sector. International companies can bring in much-needed capital, technology, and expertise.
- Trade Agreements: Iraq is a member of several international trade organizations and is exploring new trade agreements to enhance its economic ties with other countries. This can open up new markets for private businesses.
Practical Tips for Private Sector Businesses in Iraq
Navigating the Regulatory Environment
- Seek Legal Advice: Engage with local legal experts to understand the regulatory landscape and ensure compliance.
- Leverage Business Associations: Join business associations and chambers of commerce to gain insights and support from other businesses and policymakers.
Building Resilience
- Risk Management: Develop robust risk management strategies to address political and security risks. This may include insurance, contingency plans, and regular security assessments.
- Diversify Revenue Streams: To mitigate the impact of economic fluctuations, diversify your revenue streams across different sectors and markets.
Fostering Innovation
- Invest in R&D: Allocate resources to research and development to stay ahead of the curve and introduce innovative products and services.
- Collaborate with Universities: Partner with local universities and research institutions to tap into their knowledge and expertise.
Embracing Technology
- Digital Transformation: Adopt digital technologies to improve operational efficiency and customer engagement. This includes e-commerce, cloud computing, and data analytics.
- Skill Development: Invest in training and development programs to equip your workforce with the skills needed to thrive in a tech-driven economy.
Conclusion
The private sector plays a pivotal role in Iraq’s economic development, contributing to diversification, job creation, and innovation. While challenges such as political instability, bureaucratic hurdles, and infrastructure gaps persist, there are significant opportunities for businesses to thrive. Government reforms, emerging markets, and international collaboration can provide a fertile ground for growth. By navigating the regulatory environment, building resilience, fostering innovation, and embracing technology, private sector businesses can overcome obstacles and make a lasting impact on Iraq’s economy.
Call to Action
For entrepreneurs and investors looking to enter the Iraqi market, now is the time to capitalize on these opportunities. Engage with local experts, stay informed about government reforms, and leverage technology to drive success. Together, we can build a more resilient and prosperous Iraq.























































* * * Claim Free iPhone 16: https://qiblah.com.kw/index.php?3xlsrn * * * hs=fede8fc160695efc7626975f1a07a0ad* ххх*
03rd May 2025Your comment is awaiting moderation.
b9b7rt